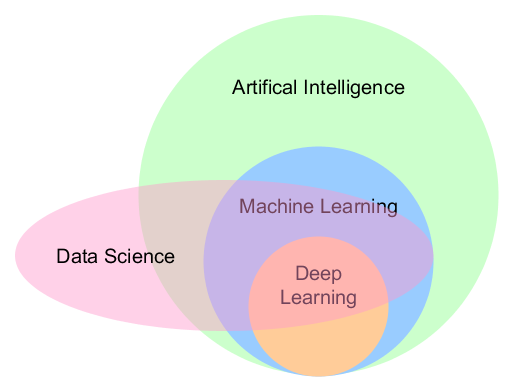
Feature Scaling
What is Feature Scaling? Feature Scaling is an important pre-processing step for some machine learning algorithms. Imagine you have three friends of whom you know the individual weight and height. You would like to deduce Christian’s t-shirt size from David’s and Julia’s by looking at the height and weight. Name Height in m Weight in…